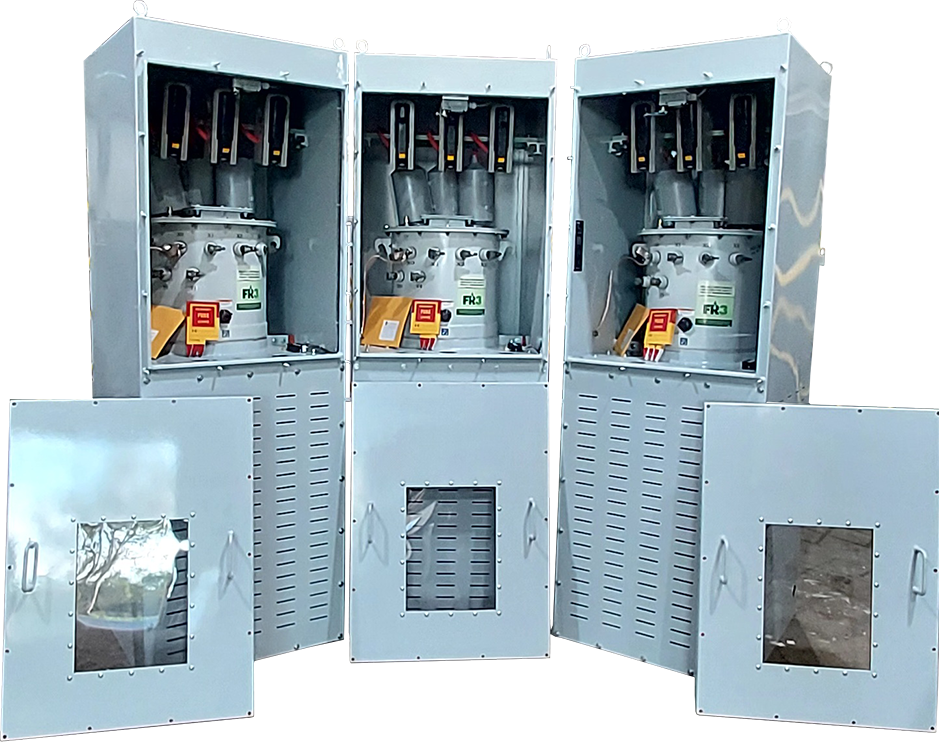
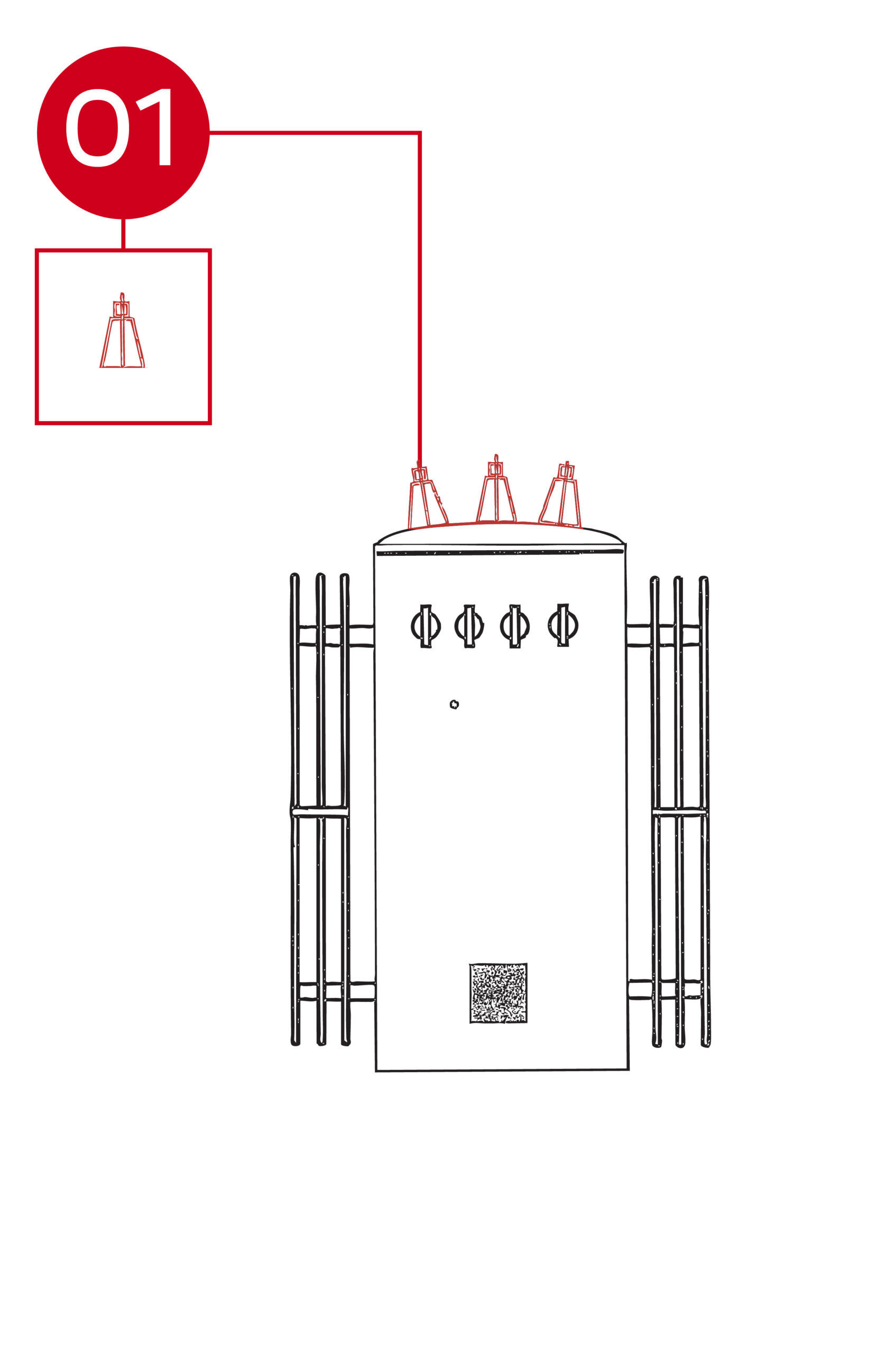
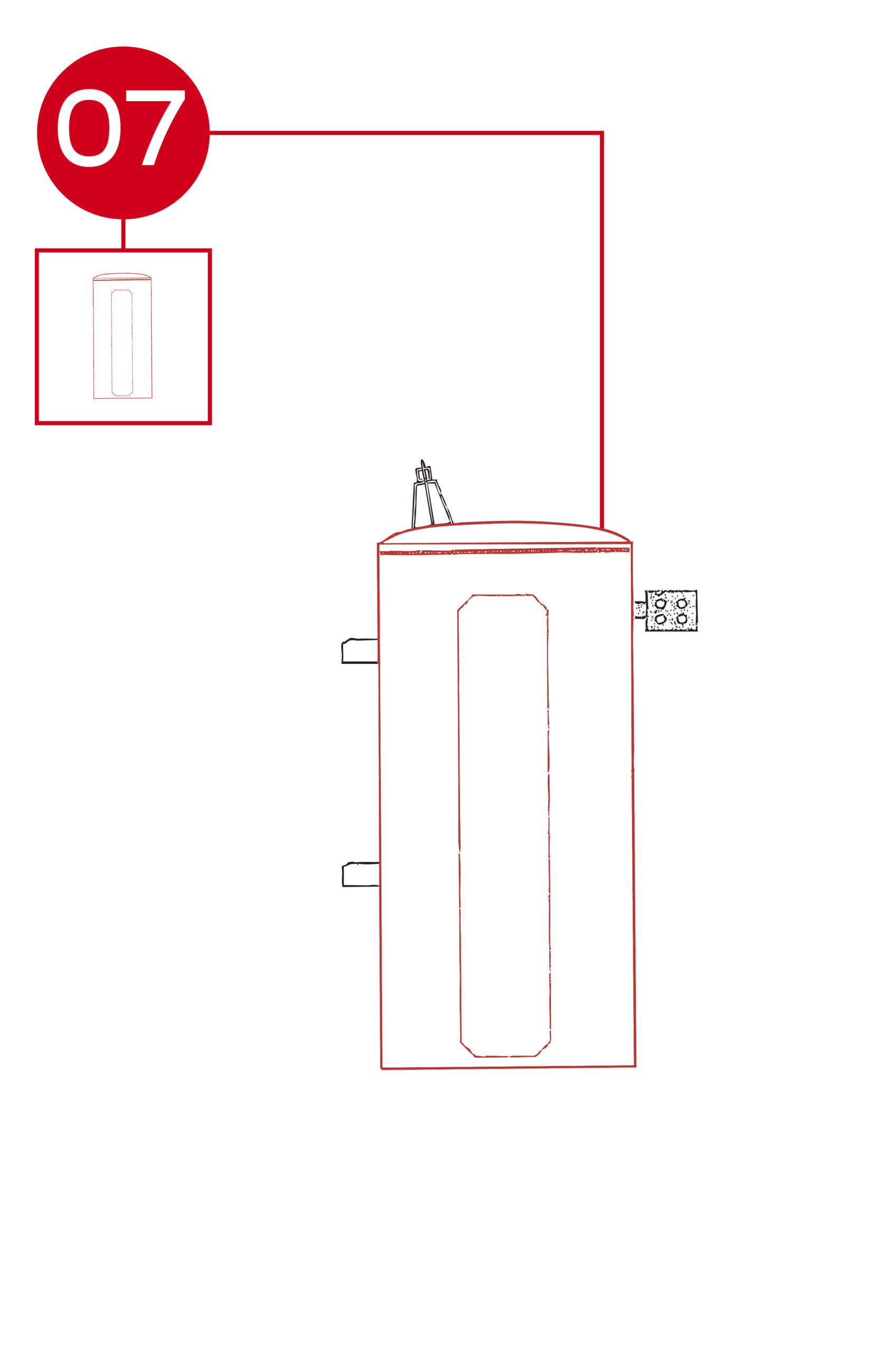
The high-voltage (HV) assembly with eyebolt connector on a three-phase pole-mount transformer provides the primary connection point for incoming distribution voltage. It is designed for secure, low-resistance attachment to overhead power lines.
- Location: Mounted on the top of the transformer tank near the high-voltage bushings, with each phase isolated from the others.
- Layout: Includes an insulated bushing connected to an internal high-voltage winding lead, terminating in a heavy-duty eyebolt connector for external line connection.
- Function: Facilitates safe and reliable electrical connection between the utility’s high-voltage supply and the transformer’s primary winding. The eyebolt design allows easy installation and removal of conductors while maintaining strong mechanical support and optimal electrical contact.
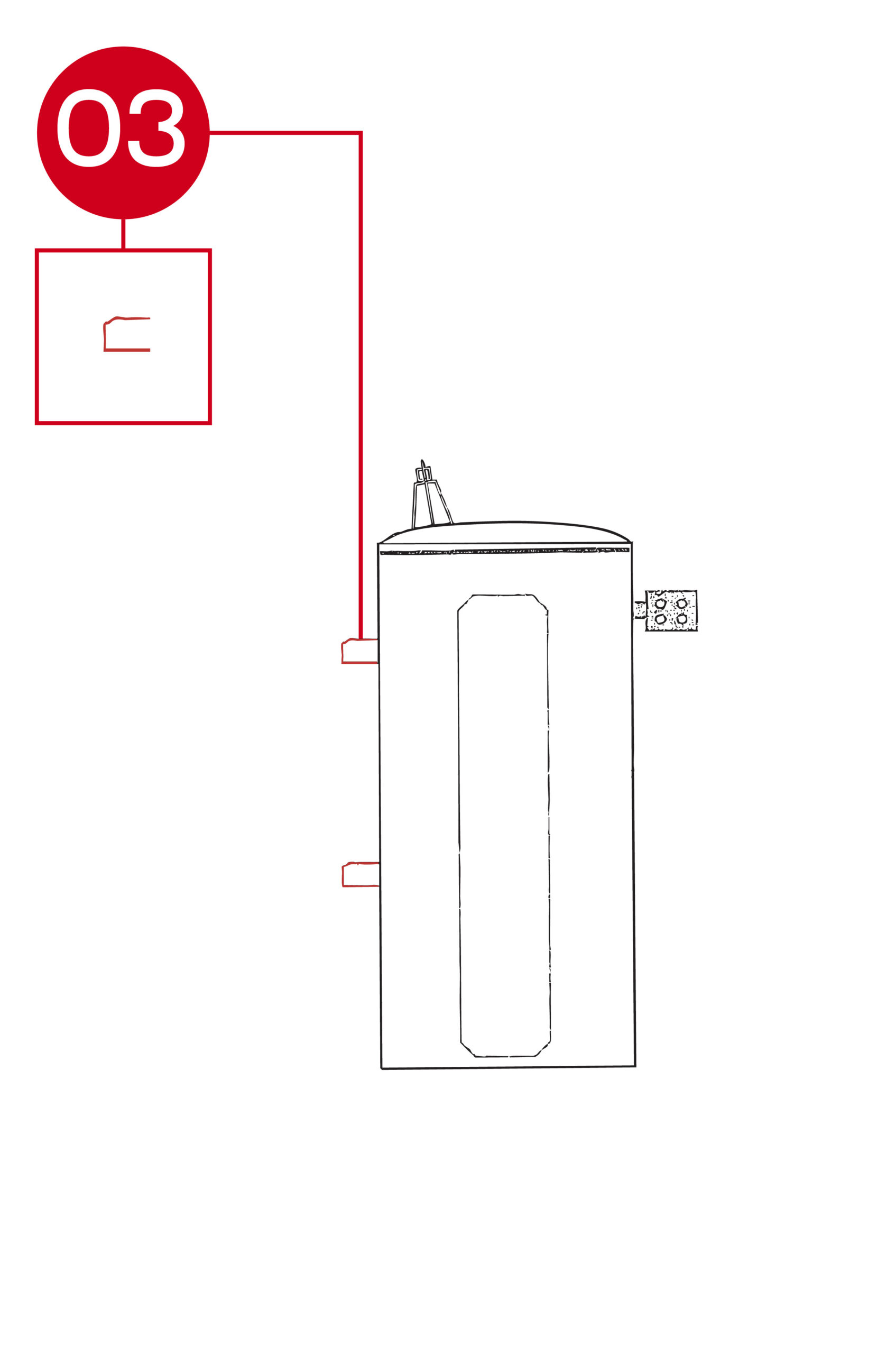
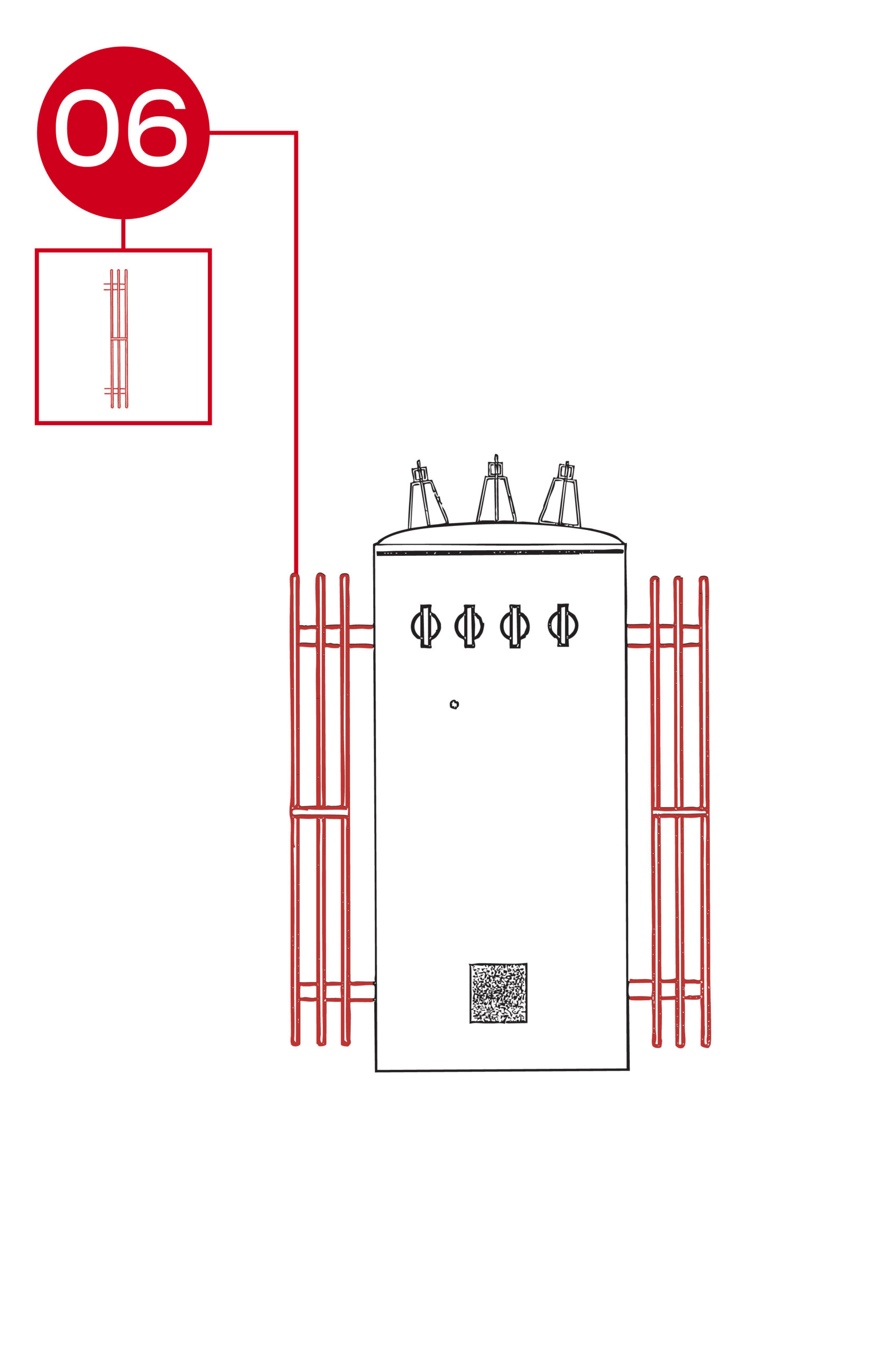
Pole-mount hangers provide the primary mechanical support system for securing the transformer to a utility pole. These heavy-duty brackets are engineered to handle the full operational weight of the transformer while maintaining proper alignment and clearance.
- Location: Welded or bolted to the upper sides of the transformer tank, positioned to evenly distribute weight and align with standard pole-mounting hardware.
- Layout: Typically consists of two steel hanger brackets or hooks with reinforced welds, designed to interface with pole crossarms, lag bolts, or suspension bands. The configuration may vary based on transformer size and mounting orientation.
- Function: Ensures stable, vibration-resistant mounting of the transformer to the pole structure. The hangers maintain proper clearance and safety spacing, reducing mechanical stress during installation and operation under load or environmental conditions.
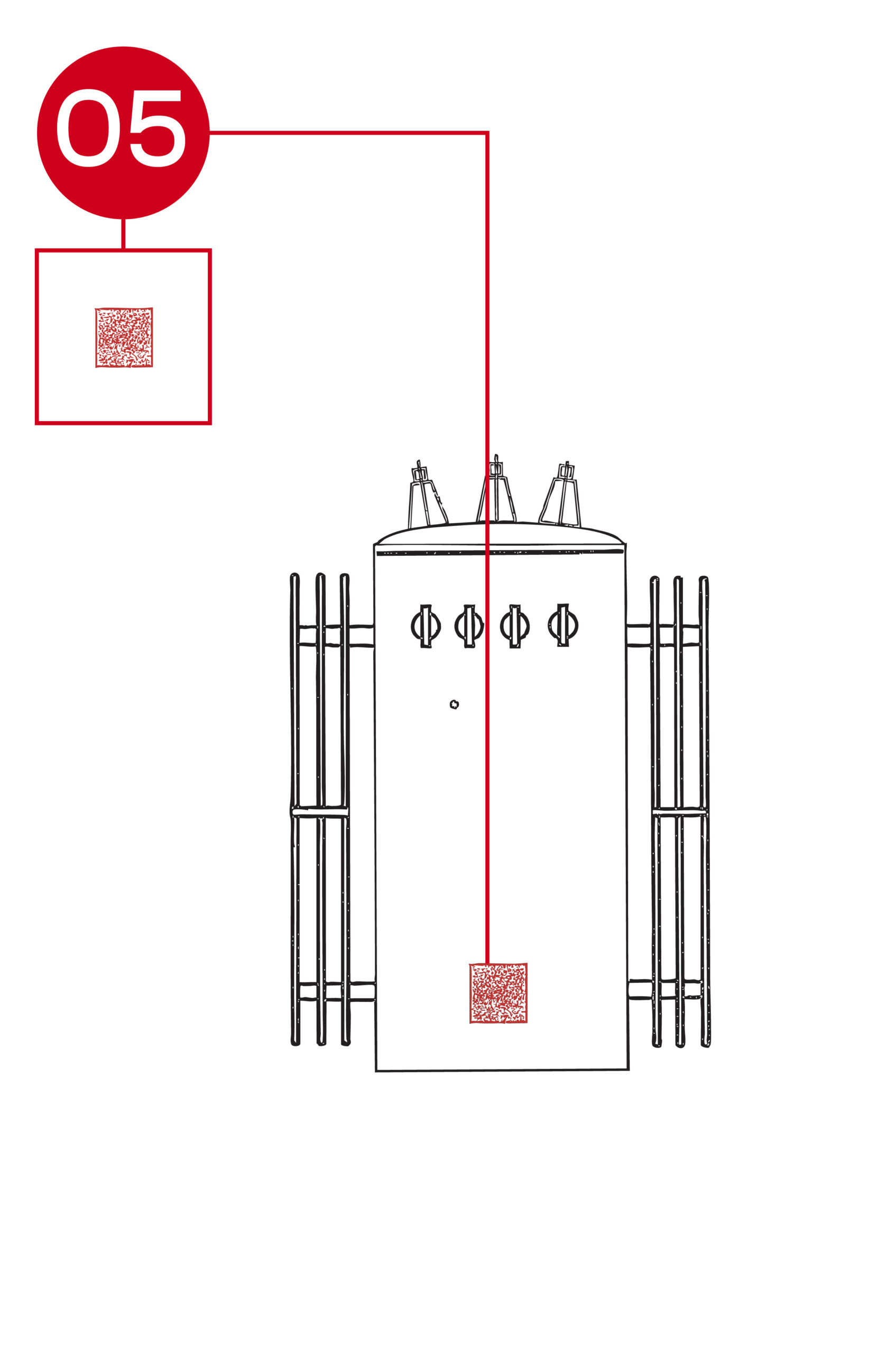
Cooling radiators on a three-phase pole-mount transformer are designed to dissipate heat generated within the transformer core and windings during operation. Efficient cooling maintains optimal oil temperature and preserves the life of insulating materials.
- Location: Mounted on the sides or rear of the transformer tank, positioned to allow natural air circulation around the radiator fins.
- Layout: Composed of a series of vertically oriented, oil-filled steel fins or panels connected to the main tank. As the transformer operates, heated oil circulates through the radiators, transferring heat to the surrounding air through convection.
- Function: Regulates the transformer’s operating temperature by increasing the surface area available for heat dissipation. This passive cooling system ensures reliable performance under load variations, prevents thermal degradation of insulation, and supports long-term service life.